Creating a Tool
Flux Bend stand alone can export bending tools as a DXF or ARV format and can import bending tools from a DXF or ARV format. All tools can be exported as a DXF format. However, only single upper tools and single lower tools can be exported as an ARV format as ARV version 4.15, no Z-bend, adapters or holders. More tool-ARV-files can be imported than exported. ARV-import exceptions are complex special tools such as e.g: hinge tools.
To create a DXF file for a new tool, a DXF file of an existing tool must be processed:
-
Export existing tool
-
Open exported DXF file
-
The DXF file must contain the following:
-
A closed form (of lines, arcs, polylines) which shows the side profile of the tool. In the drawing, this form must be at the closed polyline that is furthest to the left.
-
A point which marks the reference point of the tool. This point must be located somewhere inside the polyline of the closed profile and indicates the point from which the height of the tool is measured.
-
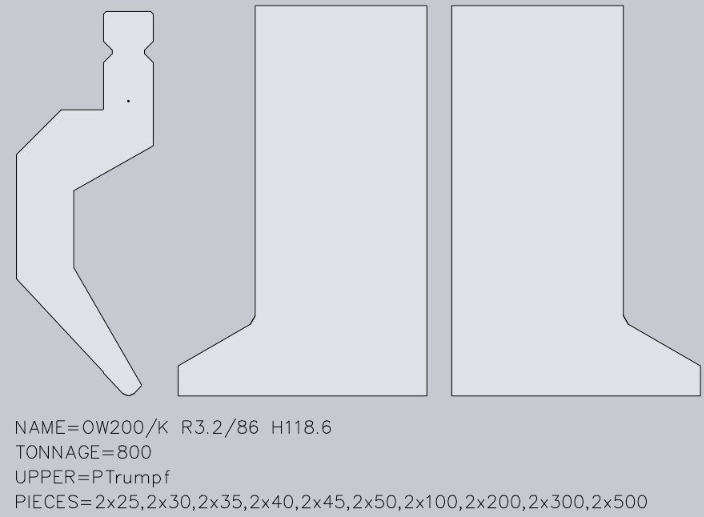
A front view is required for each tool which is not a simple rectangle in the front. These are typically left or right horn tools, but can also be user-defined tools.
-
Each front view drawing must appear on the right-hand side next to the sectional drawing, must be horizontally aligned and have the same height as the sectional drawing (currently, only the horn view is supported).
-
Additional information about the tool is displayed using text stringsThe following text strings are recognized:
-
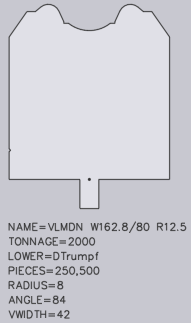
NAME=UT200/K R3.2/86 CUSTOM-A (specifies the tool name; is required)
-
TONNAGE=800 (specifies the maximum load of the tool in kN/m; this is required to avoid showing incorrect tool overload errors).
-
UPPER=PTrumpf (specifies the connection type of the upper tool to the press beam; the following connection types are supported: PTrumpf, PAmada and PEHT).
-
LOWER=DTrumpf (specifies the connection type of the lower tool; the following connection types are supported: DTrumpf, DAmada30, DAmada60, DAmadaF, DAmada2V, DAmadaQuick, DAmada90, DEHT and DAmada120)
-
PIECES=2x25, 30, 45, 50, 2x100, 200, 4x500 (this specifies the standard quantity for this tool, whereby the quantity for the left and right horn tool are defined by their sectional drawing. The list consists of a number of comma-separated quantities and, optionally, a quantity multiplier may be added in front of these. In this case the text states the following tool quantity: 2 pcs with 25 mm, 1 piece with 30 mm, 1 piece with 45 mm, 1 piece with 50 mm, 2 pcs with 100 mm, 1 piece with 200 mm and 4 pcs with 500 mm). If multiple tools with special forms (such as horn tools) are present, a text with the number of the quantity must be entered in the form:
-
-
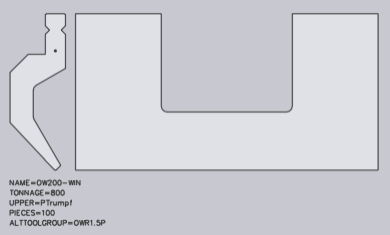
A front view can be added for window tools.
-
Export drawing
-
Import
-
Create tool ARV file for the import to the machine.
-
Activate created ARV file in the machine.
Special tools:
With Tool import, different types of special tools can be detected. These must be specified by a text in the form of FLAVOUR=XYX in the DXF file. Z-upper tools For a Z-upper tool, a text with the following format must be available in the DXF file: FLAVOR=ZBendPunch. The tool should be drawn so that the medium flat span width runs from left bottom to right top:
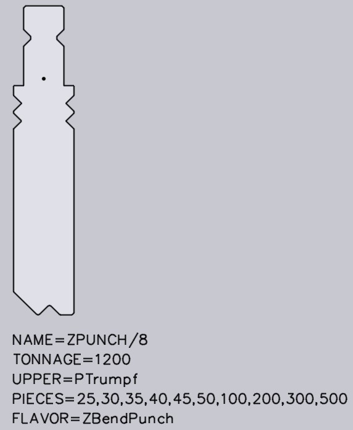
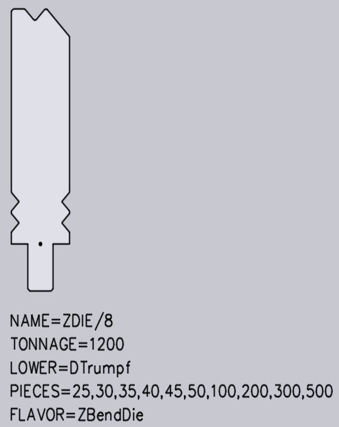
Z-lower tools:
For a Z-lower tool, a text with the following format must be available in the DXF file: FLAVOR=ZBendDie. The tool should be drawn so that the medium flat span width runs from left bottom to right top:
Upper tool adapter:
For an upper tool adapter, a text with the following format must be available in the DXF file:
-
A text such as UPPER=PTrumpf identifies the upper mounting type (PTrumpf is used if the adapter is mounted on a Trumpf machine).
-
A text such as LOWER=PEHT identifies the bottom mounting type, either type of upper tool which is mounted on the adapter.
-
A text such as HEIGHT=64 indicates the effective working height of the adapter. This is necessary because Flux Bend does not automatically detect the height of the adapter.
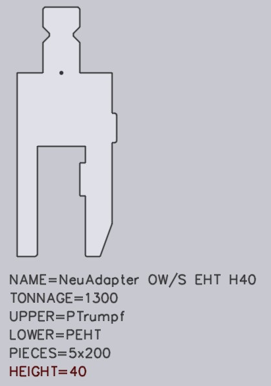
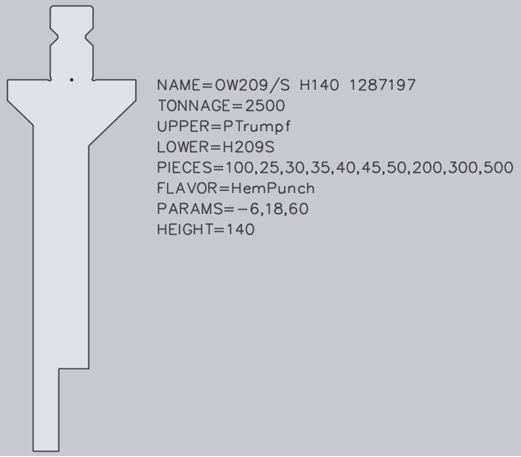
Holders are configured in exactly the same way as an upper tool adapter. However, certain holders, for example UT209/S, are also folding tools which are used to press down a fold. For these special holders, additional texts must be contained in the DXF file:
The text SPLFLAVOR=Hem. Punch identifies the adapter as a folding tool.
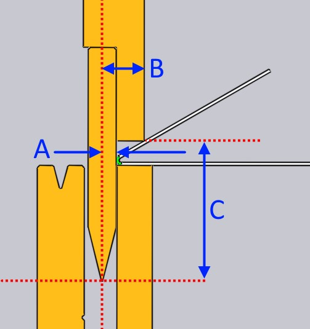
The text PARAMS=-6,18,60 identifies three parameters required for the correct simulation of the folding process. These parameters will be marked in the image below as (A), (B) and (C):
The first parameter (A) defines how far the flat vertical area of the tool is located behind the bending line. In this case, the value is negative, because the flat vertical area is located in front of the bending line.
The second parameter (B) defines how far the peak of the fold is located in front of the bending line.
The third parameter (C) defines the vertical clearance from the punching peak to the folding peak point.
Flux Bend shows messages such as Radius not specified or Angle not specified if the shape cannot be analyzed and the V-width, radius, angle etc cannot be detected as a result. In this case, the radius, angle and V-width must be added as a text.